The ALEXANDRIA  project team participated in the 14th International Conference on World Wide Web (WWW ’15) in Florence, Italy in May 2015. We contribute one full paper for the main conference and two full papers for the workshops.
project team participated in the 14th International Conference on World Wide Web (WWW ’15) in Florence, Italy in May 2015. We contribute one full paper for the main conference and two full papers for the workshops.
Contribution to the main conference:
Markus Rokicki, Sergej Zerr, Stefan Siersdorfer. “Groupsourcing: Team Competition Designs for Crowdsourcing”
Many data processing tasks such as semantic annotation of images, translation of texts in foreign languages, and labeling of training data for machine learning models require human input, and, on a large scale, can only be accurately solved using crowd based online work. Recent work shows that frameworks where crowd workers compete against each other can drastically reduce crowdsourcing costs, and outperform conventional reward schemes where the payment of online workers is proportional to the number of accomplished tasks (“pay-per-task”). In this paper, we investigate how team mechanisms can be leveraged to further improve the cost efficiency of crowdsourcing competitions. To this end, we introduce strategies for team based crowdsourcing, ranging from team formation processes where workers are randomly assigned to competing teams, over strategies involving self-organization where workers actively participate in team building, to combinations of team and individual competitions. Our large-scale experimental evaluation with more than 1,100 participants and overall 5,400 hours of work spent by crowd workers demonstrates that our team based crowdsourcing mechanisms are well accepted by online workers and lead to substantial performance boosts.

Markus Rokicki during his presentation
Read the rest of this entry »
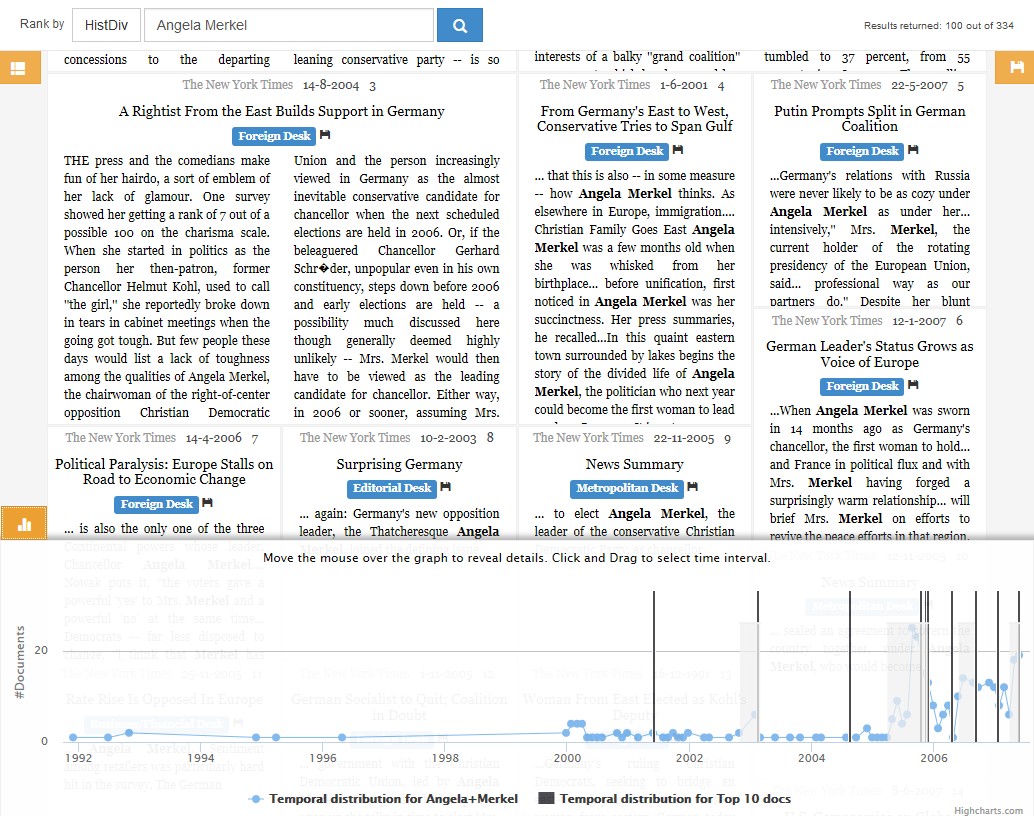 When exploring news archives, a key requirement of historians is to get an overview of their search results initially. To address this problem we developed a novel retrieval model – HistDiv – which ranks articles according to historical relevance. The Archive Exploration Engine (ArchEE) system was built to showcase how HistDiv and various other state-of-the-art retrieval models coupled with time-lines and entity filters can help users better explore large news archives.
When exploring news archives, a key requirement of historians is to get an overview of their search results initially. To address this problem we developed a novel retrieval model – HistDiv – which ranks articles according to historical relevance. The Archive Exploration Engine (ArchEE) system was built to showcase how HistDiv and various other state-of-the-art retrieval models coupled with time-lines and entity filters can help users better explore large news archives.






 project team participated in the 14th
project team participated in the 14th 